Discover how to leverage the power of kcli and libvirt to rapidly deploy a full OpenShift cluster in under 30 minutes, cutting through the complexity often associated with OpenShift installations.
Prerequisites
Server with 8+ cores, minimum of 64GB RAM (96+ for >1 worker node)
Fast IO
– dedicated NVMe libvirt storage or
– NVMe LVMCache fronting HDD (surprisingly effective!)
OS installed (tested with CentOS Stream 8)
Packages libvirt + git installed
Pull-secret (store in openshift_pull.json) obtained from https://cloud.redhat.com/openshift/install/pull-secret
Install kcli
[steve@shift ~]$ git clone https://github.com/karmab/kcli.git [steve@shift ~]$ cd kcli; ./install.sh
Configure parameters.yml
(see https://kcli.readthedocs.io/en/latest/#deploying-kubernetes-openshift-clusters)
example:-
[steve@shift ~]$ cat parameters.yml cluster: shift413 domain: shift.local version: stable tag: '4.13' ctlplanes: 3 workers:3 ctlplane_memory:16384 worker_memory:16384 ctlplane_numcpus: 8 worker_numcpus: 4
Note 1: To deploy Single Node Openshift (SNO) set ctlplanes to 1 and workers to 0.
Note 2: Even a fast Xeon with NVMe storage may have difficulty deploying more than 3 workers before the installer times out.
An RFE exists to make the timeout configurable, see:
https://access.redhat.com/solutions/6379571
https://issues.redhat.com/browse/RFE-2512
Deploy cluster
[steve@shift ~]$ kcli create kube openshift --paramfile parameters.yml $cluster
Note: openshift_pull.json and parameters.yml should be in your current working directory, or adjust above as required
Monitor Progress
If you wish to monitor progress, find IP of bootsrap node:-
[steve@shift ~]$ virsh net-dhcp-leases default Expiry Time MAC address Protocol IP address Hostname Client ID or DUID --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2023-07-19 15:48:02 52:54:00:08:41:71 ipv4 192.168.122.103/24 ocp413-ctlplane-0 01:52:54:00:08:41:71 2023-07-19 15:48:02 52:54:00:10:2a:9d ipv4 192.168.122.100/24 ocp413-ctlplane-1 01:52:54:00:10:2a:9d 2023-07-19 15:46:30 52:54:00:2b:98:2a ipv4 192.168.122.211/24 ocp413-bootstrap 01:52:54:00:2b:98:2a 2023-07-19 15:48:03 52:54:00:aa:d7:02 ipv4 192.168.122.48/24 ocp413-ctlplane-2 01:52:54:00:aa:d7:02
then ssh to bootstrap node as core user and follow instructions:-
[steve@shift ~]# ssh core@192.168.122.231 journalctl -b -f -u release-image.service -u bootkube.service
Once cluster is deployed you'll receive the following message:- INFO Waiting up to 40m0s (until 3:42PM) for the cluster at https://api.ocp413.lab.local:6443 to initialize... INFO Checking to see if there is a route at openshift-console/console... INFO Install complete! INFO To access the cluster as the system:admin user when using 'oc', run 'export KUBECONFIG=/root/.kcli/clusters/ocp413/auth/kubeconfig' INFO Access the OpenShift web-console here: https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp413.lab.local INFO Login to the console with user: "kubeadmin", and password: "qTT5W-F5Cjz-BIPx2-KWXQx" INFO Time elapsed: 16m18s Deleting ocp413-bootstrap
Note: Whilst the above credentials can be found later, it’s worthwhile making a note of the above. I save to a text file on the host.
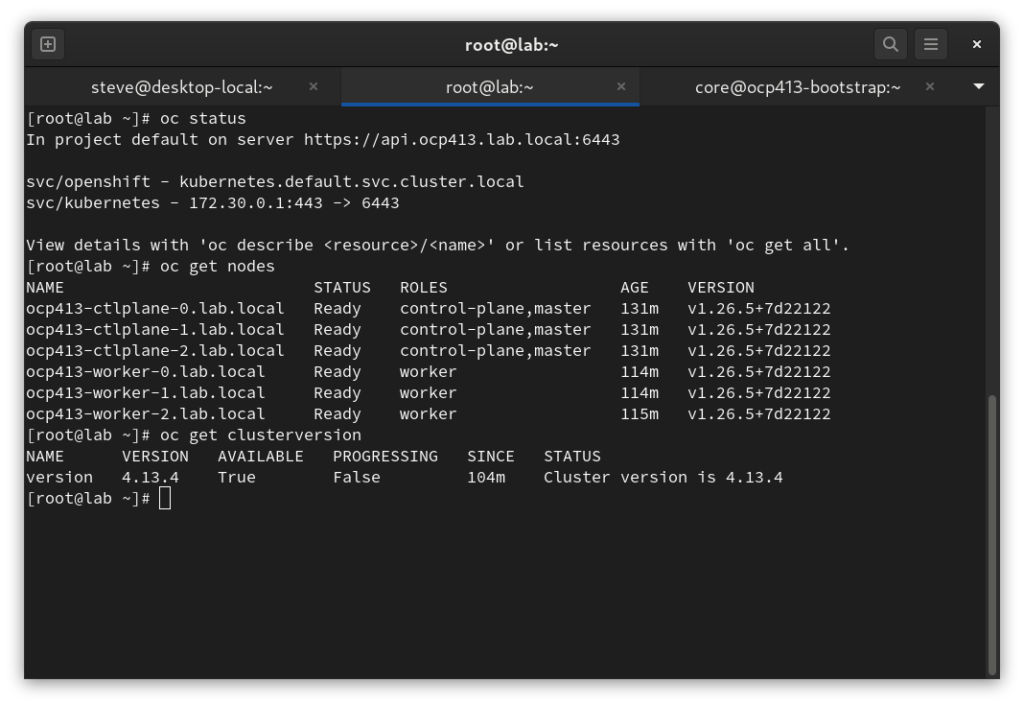
Confirm Status
[root@shift ~]# export KUBECONFIG=/root/.kcli/clusters/ocp413/auth/kubeconfig [root@lab ~]# oc status In project default on server https://api.ocp413.lab.local:6443 svc/openshift - kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local svc/kubernetes - 172.30.0.1:443 -> 6443 View details with 'oc describe <resource>/<name>' or list resources with 'oc get all'. [root@shift ~]# oc get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ocp413-ctlplane-0.lab.local Ready control-plane,master 68m v1.26.5+7d22122 ocp413-ctlplane-1.lab.local Ready control-plane,master 68m v1.26.5+7d22122 ocp413-ctlplane-2.lab.local Ready control-plane,master 68m v1.26.5+7d22122 ocp413-worker-0.lab.local Ready worker 51m v1.26.5+7d22122 ocp413-worker-1.lab.local Ready worker 51m v1.26.5+7d22122 ocp413-worker-2.lab.local Ready worker 52m v1.26.5+7d22122 [root@shift ~]# oc get clusterversion NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING SINCE STATUS version 4.13.4 True False 42m Cluster version is 4.13.4
And logging in via https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp413.lab.local/
Note: If the cluster is not installed on your workstation, it’s may be easier to install a browser on the server then forward X connections, rather than maintaining a local hosts file or modifying local DNS to catch and resolve local cluster queries:
ssh -X user@server
Success \o/
For detailed kcli documentation see: https://kcli.readthedocs.io/en/latest/

Following your guide and youtube video on creating a single node cluster, I am getting an error when running “kcli create”. See below:
Using installer version 4.15.14
Grabbing image rhcos-415.92.202402201450-0-openstack.x86_64.qcow2 from url https://rhcos.mirror.openshift.com/art/storage/prod/streams/4.15-9.2/builds/415.92.202402201450-0/x86_64/rhcos-415.92.202402201450-0-openstack.x86_64.qcow2.gz
Image rhcos-415.92.202402201450-0-openstack.x86_64.qcow2 not Added because Pool default not found
Pool default not found
Any ideas as to why this is happening? I’m running fedora server 40 and trying to install SNO 4.15.
hello, just need to create the pool first, as stated in the doc, with
kcli create pool -p /var/lib/libvirt/images default